Biology:Microbial rhodopsin

| Archaeal/bacterial/fungal rhodopsins | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Bacteriorhodopsin trimer | |||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| Symbol | Bac_rhodopsin | ||||||||
| Pfam | PF01036 | ||||||||
| InterPro | IPR001425 | ||||||||
| SMART | SM01021 | ||||||||
| PROSITE | PDOC00291 | ||||||||
| SCOP2 | 2brd / SCOPe / SUPFAM | ||||||||
| TCDB | 3.E.1 | ||||||||
| OPM superfamily | 6 | ||||||||
| OPM protein | 1vgo | ||||||||
| |||||||||
Microbial rhodopsins, also known as bacterial rhodopsins, are retinal-binding proteins that provide light-dependent ion transport and sensory functions in halophilic[2][3] and other bacteria. They are integral membrane proteins with seven transmembrane helices, the last of which contains the attachment point (a conserved lysine) for retinal.
This protein family includes light-driven proton pumps, ion pumps and ion channels, as well as light sensors. For example, the proteins from halobacteria include bacteriorhodopsin and archaerhodopsin, which are light-driven proton pumps; halorhodopsin, a light-driven chloride pump; and sensory rhodopsin, which mediates both photoattractant (in the red) and photophobic (in the ultra-violet) responses. Proteins from other bacteria include proteorhodopsin.
As their name indicates, microbial rhodopsins are found in Archaea and Bacteria, and also in Eukaryota (such as algae) and viruses; although they are rare in complex multicellular organisms.[4][5]
Nomenclature
Rhodopsin was originally a synonym for "visual purple", a visual pigment (light-sensitive molecule) found in the retinas of frogs and other vertebrates, used for dim-light vision, and usually found in rod cells. This is still the meaning of rhodopsin in the narrow sense, any protein evolutionarily homologous to this protein. In a broad non-genetic sense, rhodopsin refers to any molecule, whether related by genetic descent or not (mostly not), consisting of an opsin and a chromophore (generally a variant of retinal). All animal rhodopsins arose (by gene duplication and divergence) late in the history of the large G-protein coupled receptor (GPCR) gene family, which itself arose after the divergence of plants, fungi, choanoflagellates and sponges from the earliest animals. The retinal chromophore is found solely in the opsin branch of this large gene family, meaning its occurrence elsewhere represents convergent evolution, not homology. Microbial rhodopsins are, by sequence, very different from any of the GPCR families.[6]
The term bacterial rhodopsin originally referred to the first microbial rhodopsin discovered, known today as bacteriorhodopsin. The first bacteriorhodopsin turned out to be of archaeal origin, from Halobacterium salinarum.[7] Since then, other microbial rhodopsins have been discovered, rendering the term bacterial rhodopsin ambiguous.[8][9]
Table
Below is a list of some of the more well-known microbial rhodopsins and some of their properties.
| Function | Name | Abbr. | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| proton pump (H+) | bacteriorhodopsin | BR | [10] |
| proton pump (H+) | proteorhodopsin | PR | [10] |
| proton pump (H+) | archaerhodopsin | Arch | [11] |
| proton pump (H+) | xanthorhodopsin | xR | [12] |
| proton pump (H+) | Gloeobacter rhodopsin | GR | [13] |
| cation channel (+) | channelrhodopsin | ChR | [14] |
| cation pump (Na+) | Krokinobacter eikastus rhodopsin 2 | KR2 | [15] |
| anion pump (Cl-) | halorhodopsin | HR | [10] |
| photosensor | sensory rhodopsin I | SR-I | [10] |
| photosensor | sensory rhodopsin II | SR-II | [10] |
| photosensor | Neurospora opsin I | NOP-I | [14][16] |
| light-activated enzyme | rhodopsin guanylyl cyclase | RhGC | [17] |
The Ion-Translocating Microbial Rhodopsin Family
The Ion-translocating Microbial Rhodopsin (MR) Family (TC# 3.E.1) is a member of the TOG Superfamily of secondary carriers. Members of the MR family catalyze light-driven ion translocation across microbial cytoplasmic membranes or serve as light receptors. Most proteins of the MR family are all of about the same size (250-350 amino acyl residues) and possess seven transmembrane helical spanners with their N-termini on the outside and their C-termini on the inside. There are 9 subfamilies in the MR family:[18]
- Bacteriorhodopsins pump protons out of the cell;
- Halorhodopsins pump chloride (and other anions such as bromide, iodide and nitrate) into the cell;
- Sensory rhodopsins, which normally function as receptors for phototactic behavior, are capable of pumping protons out of the cell if dissociated from their transducer proteins;
- the Fungal Chaperones are stress-induced proteins of ill-defined biochemical function, but this subfamily also includes a H+-pumping rhodopsin;[19]
- the bacterial rhodopsin, called Proteorhodopsin, is a light-driven proton pump that functions as does bacteriorhodopsins;
- the Neurospora crassa retinal-containing receptor serves as a photoreceptor (Neurospora ospin I);[20]
- the green algal light-gated proton channel, Channelrhodopsin-1;
- Sensory rhodopsins from cyanobacteria.
- Light-activated rhodopsin/guanylyl cyclase
A phylogenetic analysis of microbial rhodopsins and a detailed analysis of potential examples of horizontal gene transfer have been published.[21]
Structure
Among the high resolution structures for members of the MR Family are the archaeal proteins, bacteriorhodopsin,[22] archaerhodopsin,[23] sensory rhodopsin II,[24] halorhodopsin,[25] as well as an Anabaena cyanobacterial sensory rhodopsin (TC# 3.E.1.1.6)[26] and others.
Function
The association of sensory rhodopsins with their transducer proteins appears to determine whether they function as transporters or receptors. Association of a sensory rhodopsin receptor with its transducer occurs via the transmembrane helical domains of the two interacting proteins. There are two sensory rhodopsins in any one halophilic archaeon, one (SRI) that responds positively to orange light but negatively to blue light, the other (SRII) that responds only negatively to blue light. Each transducer is specific for its cognate receptor. An x-ray structure of SRII complexed with its transducer (HtrII) at 1.94 Å resolution is available (1H2S).[27] Molecular and evolutionary aspects of the light-signal transduction by microbial sensory receptors have been reviewed.[28]
Homologues
Homologues include putative fungal chaperone proteins, a retinal-containing rhodopsin from Neurospora crassa,[29] a H+-pumping rhodopsin from Leptosphaeria maculans,[19] retinal-containing proton pumps isolated from marine bacteria,[30] a green light-activated photoreceptor in cyanobacteria that does not pump ions and interacts with a small (14 kDa) soluble transducer protein [26][31] and light-gated H+ channels from the green alga, Chlamydomonas reinhardtii.[32] The N. crassa NOP-1 protein exhibits a photocycle and conserved H+ translocation residues that suggest that this putative photoreceptor is a slow H+ pump.[19][33][34]
Most of the MR family homologues in yeast and fungi are of about the same size and topology as the archaeal proteins (283-344 amino acyl residues; 7 putative transmembrane α-helical segments), but they are heat shock- and toxic solvent-induced proteins of unknown biochemical function. They have been suggested to function as pmf-driven chaperones that fold extracellular proteins, but only indirect evidence supports this postulate.[20] The MR family is distantly related to the 7 TMS LCT family (TC# 2.A.43).[20] Representative members of MR family can be found in the Transporter Classification Database.
Bacteriorhodopsin
Bacteriorhodopsin pumps one H+ ion, from the cytosol to the extracellular medium, per photon absorbed. Specific transport mechanisms and pathways have been proposed.[25][35][36] The mechanism involves:
- photo-isomerization of the retinal and its initial configurational changes,
- deprotonation of the retinal Schiff base and the coupled release of a proton to the extracellular membrane surface,
- the switch event that allows reprotonation of the Schiff base from the cytoplasmic side.
Six structural models describe the transformations of the retinal and its interaction with water 402, Asp85, and Asp212 in atomic detail, as well as the displacements of functional residues farther from the Schiff base. The changes provide rationales for how relaxation of the distorted retinal causes movements of water and protein atoms that result in vectorial proton transfers to and from the Schiff base.[35] Helix deformation is coupled to vectorial proton transport in the photocycle of bacteriorhodopsin.[37]
Most residues participating in the trimerization are not conserved in bacteriorhodopsin, a homologous protein capable of forming a trimeric structure in the absence of bacterioruberin. Despite a large alteration in the amino acid sequence, the shape of the intratrimer hydrophobic space filled by lipids is highly conserved between archaerhodopsin-2 and bacteriorhodopsin. Since a transmembrane helix facing this space undergoes a large conformational change during the proton pumping cycle, it is feasible that trimerization is an important strategy to capture special lipid components that are relevant to the protein activity.[38]
Archaerhodopsin
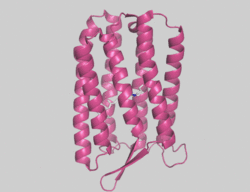
Archaerhodopsins are light-driven H+ ion transporters. They differ from bacteriorhodopsin in that the claret membrane, in which they are expressed, includes bacterioruberin, a second chromophore thought to protect against photobleaching. Bacteriorhodopsin also lacks the omega loop structure that has been observed at the N-terminus of the structures of several archaerhodopsins.
Archaerhodopsin-2 (AR2) is found in the claret membrane of Halorubrum sp. It is a light-driven proton pump. Trigonal and hexagonal crystals revealed that trimers are arranged on a honeycomb lattice.[38] In these crystals, bacterioruberin binds to crevices between the subunits of the trimer. The polyene chain of the second chromophore is inclined from the membrane normal by an angle of about 20 degrees and, on the cytoplasmic side, it is surrounded by helices AB and DE of neighboring subunits. This peculiar binding mode suggests that bacterioruberin plays a structural role for the trimerization of AR2. When compared with the aR2 structure in another crystal form containing no bacterioruberin, the proton release channel takes a more closed conformation in the P321 or P6(3) crystal; i.e., the native conformation of protein is stabilized in the trimeric protein-bacterioruberin complex.
Mutants of Archaerhodopsin-3 (AR3) are widely used as tools in optogenetics for neuroscience research.[39]
Channelrhodopsins
Channelrhodopsin-1 (ChR1) or channelopsin-1 (Chop1; Cop3; CSOA) of C. reinhardtii is closely related to the archaeal sensory rhodopsins. It has 712 aas with a signal peptide, followed by a short amphipathic region, and then a hydrophobic N-terminal domain with seven probable TMSs (residues 76-309) followed by a long hydrophilic C-terminal domain of about 400 residues. Part of the C-terminal hydrophilic domain is homologous to intersection (EH and SH3 domain protein 1A) of animals (AAD30271).
Chop1 serves as a light-gated proton channel and mediates phototaxis and photophobic responses in green algae.[32] Based on this phenotype, Chop1 could be assigned to TC category #1.A, but because it belongs to a family in which well-characterized homologues catalyze active ion transport, it is assigned to the MR family. Expression of the chop1 gene, or a truncated form of that gene encoding only the hydrophobic core (residues 1-346 or 1–517) in frog oocytes in the presence of all-trans retinal produces a light-gated conductance that shows characteristics of a channel passively but selectively permeable to protons. This channel activity probably generates bioelectric currents.[32]
A homologue of ChR1 in C. reinhardtii is channelrhodopsin-2 (ChR2; Chop2; Cop4; CSOB). This protein is 57% identical, 10% similar to ChR1. It forms a cation-selective ion channel activated by light absorption. It transports both monovalent and divalent cations. It desensitizes to a small conductance in continuous light. Recovery from desensitization is accelerated by extracellular H+ and a negative membrane potential. It may be a photoreceptor for dark adapted cells.[40] A transient increase in hydration of transmembrane α-helices with a t(1/2) = 60 μs tallies with the onset of cation permeation. Aspartate 253 accepts the proton released by the Schiff base (t(1/2) = 10 μs), with the latter being reprotonated by aspartic acid 156 (t(1/2) = 2 ms). The internal proton acceptor and donor groups, corresponding to D212 and D115 in bacteriorhodopsin, are clearly different from other microbial rhodopsins, indicating that their spatial positions in the protein were relocated during evolution. E90 deprotonates exclusively in the nonconductive state. The observed proton transfer reactions and the protein conformational changes relate to the gating of the cation channel.[41]
Halorhodopsins
Bacteriorhodopsin pumps one Cl− ion, from the extracellular medium into the cytosol, per photon absorbed. Although the ions move in the opposite direction, the current generated (as defined by the movement of positive charge) is the same as for bacteriorhodopsin and the archaerhodopsins.
Marine Bacterial Rhodopsin
A marine bacterial rhodopsin has been reported to function as a proton pump. However, it also resembles sensory rhodopsin II of archaea as well as an Orf from the fungus Leptosphaeria maculans (AF290180). These proteins exhibit 20-30% identity with each other.
Transport Reaction
The generalized transport reaction for bacterio- and sensory rhodopsins is:[18]
- H+ (in) + hν → H+ (out).
That for halorhodopsin is:
- Cl− (out) + hν → Cl− (in).
See also
References
- ↑ "Molecular ecology of extremely halophilic Archaea and Bacteria". FEMS Microbiology Ecology 39 (1): 1–7. January 2002. doi:10.1111/j.1574-6941.2002.tb00900.x. PMID 19709178. Bibcode: 2002FEMME..39....1O.
- ↑ "Two pumps, one principle: light-driven ion transport in halobacteria". Trends in Biochemical Sciences 14 (2): 57–61. February 1989. doi:10.1016/0968-0004(89)90044-3. PMID 2468194.
- ↑ "Primary structure of sensory rhodopsin I, a prokaryotic photoreceptor". The EMBO Journal 8 (13): 3963–71. December 1989. doi:10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08579.x. PMID 2591367.
- ↑ "MicRhoDE: a curated database for the analysis of microbial rhodopsin diversity and evolution". Database 2015: bav080. 2015. doi:10.1093/database/bav080. PMID 26286928.
- ↑ Optogenetics: Light-Sensing Proteins and Their Applications. Springe r. 5 June 2015. pp. 3–4. ISBN 978-4-431-55516-2. https://books.google.com/books?id=5M3WCQAAQBAJ&pg=PA3. Retrieved 30 September 2015.
- ↑ "Independent HHsearch, Needleman--Wunsch-based, and motif analyses reveal the overall hierarchy for most of the G protein-coupled receptor families". Molecular Biology and Evolution 28 (9): 2471–80. September 2011. doi:10.1093/molbev/msr061. PMID 21402729.
- ↑ "Enlightening the life sciences: the history of halobacterial and microbial rhodopsin research". FEMS Microbiology Reviews 35 (6): 1082–99. November 2011. doi:10.1111/j.1574-6976.2011.00281.x. PMID 21623844.
- ↑ "rhodopsin, n.". OED Online. Oxford University Press. 19 December 2012. http://www.oed.com/view/Entry/165304.
- ↑ Medical Neurobiology. OUP USA. 26 May 2011. p. 375. ISBN 978-0-19-533997-0. https://books.google.com/books?id=IcRqgPnstUUC&pg=PA375. Retrieved 21 September 2015.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 10.2 10.3 10.4 "Functional characterization of flavobacteria rhodopsins reveals a unique class of light-driven chloride pump in bacteria". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 111 (18): 6732–7. May 2014. doi:10.1073/pnas.1403051111. PMID 24706784. Bibcode: 2014PNAS..111.6732Y.
- ↑ "The microbial opsin family of optogenetic tools". Cell 147 (7): 1446–57. December 2011. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2011.12.004. PMID 22196724.
- ↑ "A microbial rhodopsin with a unique retinal composition shows both sensory rhodopsin II and bacteriorhodopsin-like properties". The Journal of Biological Chemistry 286 (8): 5967–76. February 2011. doi:10.1074/jbc.M110.190058. PMID 21135094.
- ↑ "X-ray Crystallographic Structure and Oligomerization of Gloeobacter Rhodopsin". Scientific Reports 9 (1): 11283. August 2019. doi:10.1038/s41598-019-47445-5. PMID 31375689. Bibcode: 2019NatSR...911283M.
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 "Plant and fungal photopigments". Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Membrane Transport and Signaling 1 (4): 411–432. 2012. doi:10.1002/wmts.36. ISSN 2190-460X.
- ↑ "Structural basis for Na(+) transport mechanism by a light-driven Na(+) pump". Nature 521 (7550): 48–53. May 2015. doi:10.1038/nature14322. PMID 25849775. Bibcode: 2015Natur.521...48K.
- ↑ "Regulation of transcription by light in Neurospora crassa: A model for fungal photobiology?". Fungal Biology Reviews 27 (1): 10–18. 2013. doi:10.1016/j.fbr.2013.02.004. ISSN 1749-4613. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/257691686.
- ↑ "The rhodopsin-guanylyl cyclase of the aquatic fungus Blastocladiella emersonii enables fast optical control of cGMP signaling". Science Signaling 8 (389): rs8. August 2015. doi:10.1126/scisignal.aab0611. PMID 26268609. https://zenodo.org/record/895813.
- ↑ 18.0 18.1 "3.E.1 The Ion-translocating Microbial Rhodopsin (MR) Family". Saier Lab Bioinformatics Group / SDSC. http://www.tcdb.org/search/result.php?tc=3.E.1#ref9955.
- ↑ 19.0 19.1 19.2 "Leptosphaeria rhodopsin: bacteriorhodopsin-like proton pump from a eukaryote". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 102 (19): 6879–83. May 2005. doi:10.1073/pnas.0409659102. PMID 15860584. Bibcode: 2005PNAS..102.6879W.
- ↑ 20.0 20.1 20.2 "Homologues of archaeal rhodopsins in plants, animals and fungi: structural and functional predications for a putative fungal chaperone protein". Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Biomembranes 1511 (2): 206–23. April 2001. doi:10.1016/s0005-2736(00)00389-8. PMID 11286964.
- ↑ "Microbial rhodopsins: functional versatility and genetic mobility". Trends in Microbiology 14 (11): 463–9. November 2006. doi:10.1016/j.tim.2006.09.006. PMID 17008099.
- ↑ "Structural changes in bacteriorhodopsin during ion transport at 2 angstrom resolution". Science 286 (5438): 255–61. October 1999. doi:10.1126/science.286.5438.255. PMID 10514362.
- ↑ 23.0 23.1 "Structures of the archaerhodopsin-3 transporter reveal that disordering of internal water networks underpins receptor sensitization". Nature Communications 12 (1): 629. January 2021. doi:10.1038/s41467-020-20596-0. PMID 33504778. Bibcode: 2021NatCo..12..629B.
- ↑ "X-ray structure of sensory rhodopsin II at 2.1-A resolution". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 98 (18): 10131–6. August 2001. doi:10.1073/pnas.181203898. PMID 11504917. Bibcode: 2001PNAS...9810131R.
- ↑ 25.0 25.1 "Structure of the light-driven chloride pump halorhodopsin at 1.8 A resolution". Science 288 (5470): 1390–6. May 2000. doi:10.1126/science.288.5470.1390. PMID 10827943. Bibcode: 2000Sci...288.1390K.
- ↑ 26.0 26.1 "Anabaena sensory rhodopsin: a photochromic color sensor at 2.0 A". Science 306 (5700): 1390–3. November 2004. doi:10.1126/science.1103943. PMID 15459346. Bibcode: 2004Sci...306.1390V.
- ↑ "Molecular basis of transmembrane signalling by sensory rhodopsin II-transducer complex". Nature 419 (6906): 484–7. October 2002. doi:10.1038/nature01109. PMID 12368857. Bibcode: 2002Natur.419..484G.
- ↑ "Molecular and evolutionary aspects of microbial sensory rhodopsins". Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Bioenergetics 1837 (5): 562–77. May 2014. doi:10.1016/j.bbabio.2013.05.005. PMID 23732219.
- ↑ "Heme histidine ligands within gp91(phox) modulate proton conduction by the phagocyte NADPH oxidase". The Journal of Biological Chemistry 276 (32): 30277–84. August 2001. doi:10.1074/jbc.M010438200. PMID 11389135.
- ↑ "Bacterial rhodopsin: evidence for a new type of phototrophy in the sea". Science 289 (5486): 1902–6. September 2000. doi:10.1126/science.289.5486.1902. PMID 10988064. Bibcode: 2000Sci...289.1902B.
- ↑ "Demonstration of a sensory rhodopsin in eubacteria". Molecular Microbiology 47 (6): 1513–22. March 2003. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2958.2003.03395.x. PMID 12622809.
- ↑ 32.0 32.1 32.2 "Channelrhodopsin-1: a light-gated proton channel in green algae". Science 296 (5577): 2395–8. June 2002. doi:10.1126/science.1072068. PMID 12089443. Bibcode: 2002Sci...296.2395N.
- ↑ "Photochemical reaction cycle and proton transfers in Neurospora rhodopsin". The Journal of Biological Chemistry 276 (35): 32495–505. August 2001. doi:10.1074/jbc.M102652200. PMID 11435422.
- ↑ "Fungal rhodopsins and opsin-related proteins: eukaryotic homologues of bacteriorhodopsin with unknown functions". Photochemical & Photobiological Sciences 3 (6): 555–65. June 2004. doi:10.1039/b315527g. PMID 15170485.
- ↑ 35.0 35.1 "Mechanism of proton transport in bacteriorhodopsin from crystallographic structures of the K, L, M1, M2, and M2' intermediates of the photocycle". Journal of Molecular Biology 328 (2): 439–50. April 2003. doi:10.1016/s0022-2836(03)00263-8. PMID 12691752.
- ↑ "Crystallographic structures of the M and N intermediates of bacteriorhodopsin: assembly of a hydrogen-bonded chain of water molecules between Asp-96 and the retinal Schiff base". Journal of Molecular Biology 330 (3): 553–70. July 2003. doi:10.1016/s0022-2836(03)00576-x. PMID 12842471.
- ↑ "Helix deformation is coupled to vectorial proton transport in the photocycle of bacteriorhodopsin". Nature 406 (6796): 645–8. August 2000. doi:10.1038/35020599. PMID 10949307. Bibcode: 2000Natur.406..645R.
- ↑ 38.0 38.1 "Structural role of bacterioruberin in the trimeric structure of archaerhodopsin-2". Journal of Molecular Biology 375 (5): 1267–81. February 2008. doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2007.11.039. PMID 18082767.
- ↑ "Archaerhodopsin variants with enhanced voltage-sensitive fluorescence in mammalian and Caenorhabditis elegans neurons". Nature Communications 5: 4894. September 2014. doi:10.1038/ncomms5894. PMID 25222271. Bibcode: 2014NatCo...5.4894F.
- ↑ "Channelrhodopsin-2, a directly light-gated cation-selective membrane channel". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 100 (24): 13940–5. November 2003. doi:10.1073/pnas.1936192100. PMID 14615590. Bibcode: 2003PNAS..10013940N.
- ↑ "Transient protonation changes in channelrhodopsin-2 and their relevance to channel gating". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 110 (14): E1273-81. April 2013. doi:10.1073/pnas.1219502110. PMID 23509282. Bibcode: 2013PNAS..110E1273L.
ru:Бактериородопсин
 |

